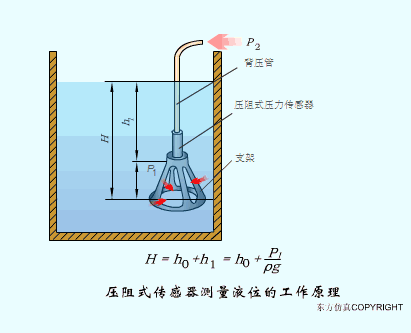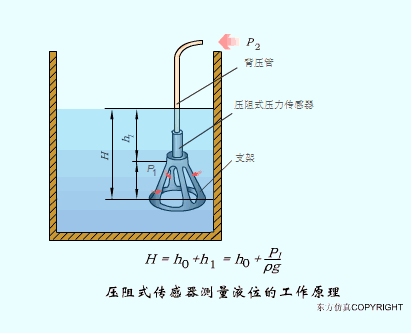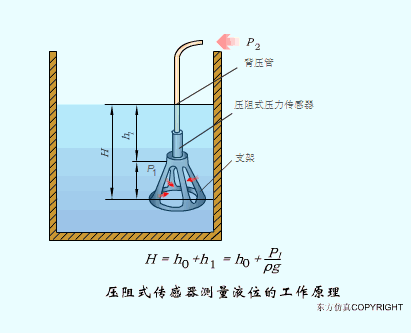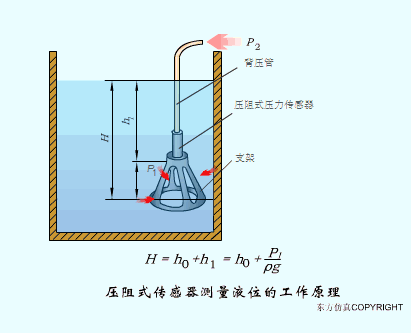
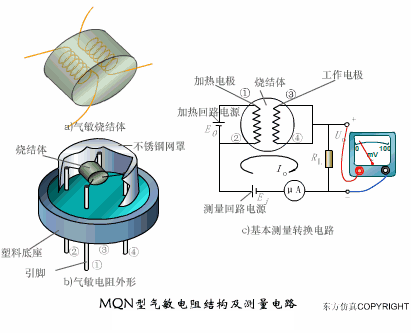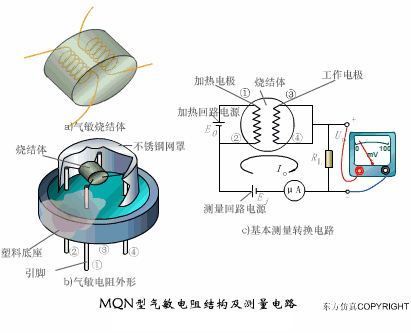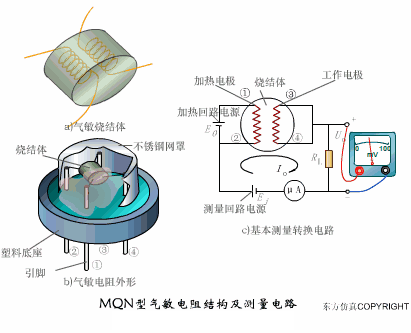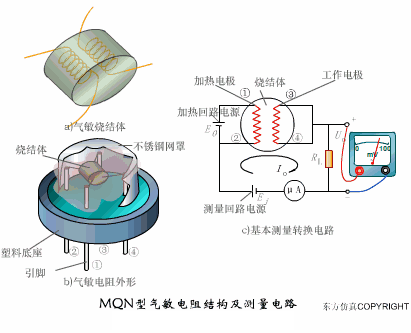
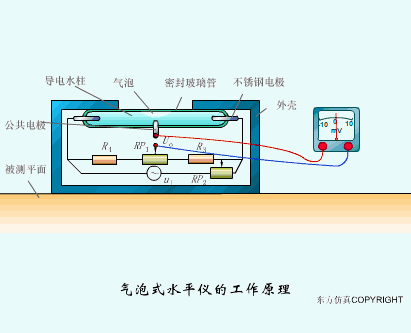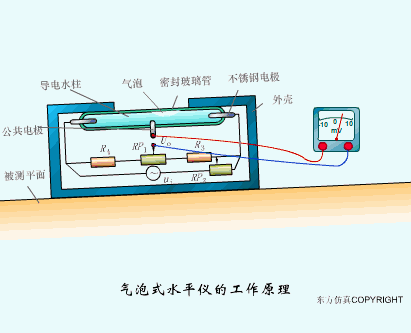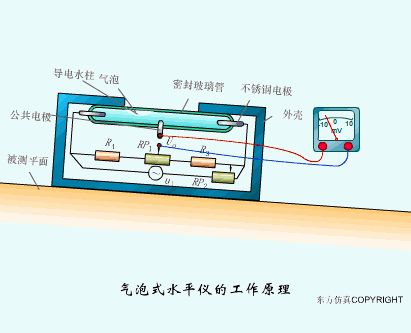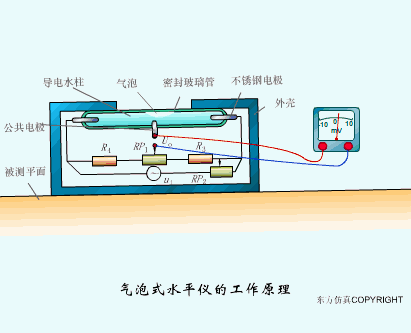
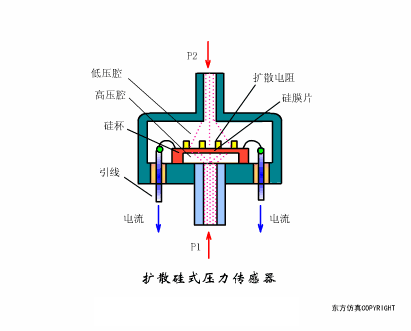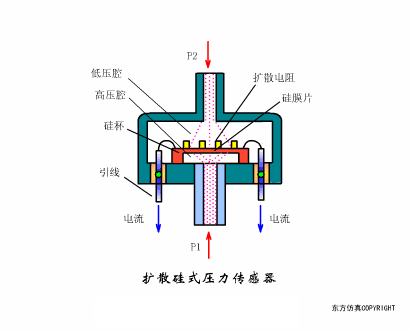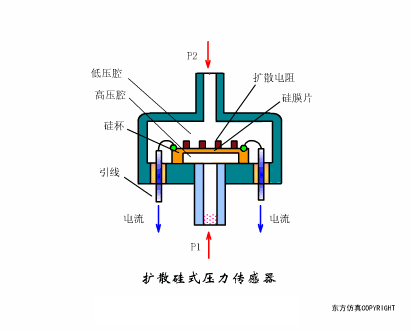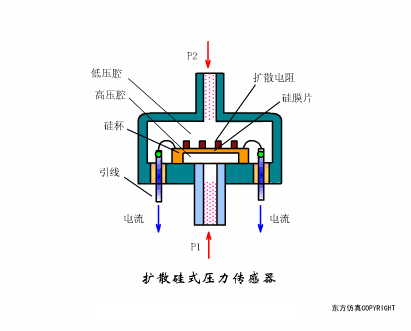
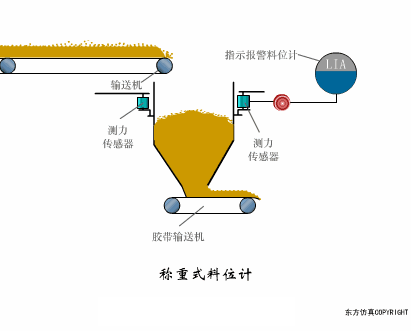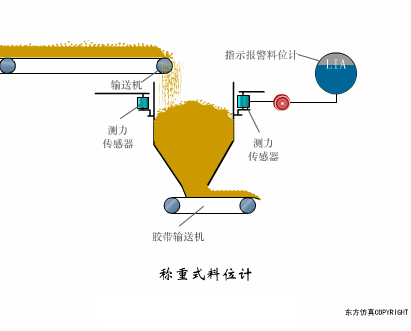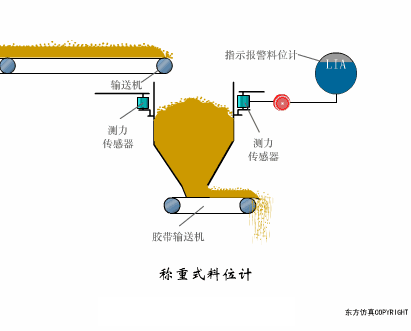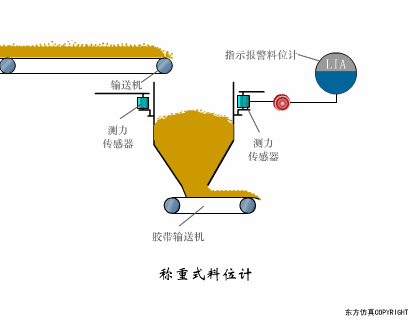
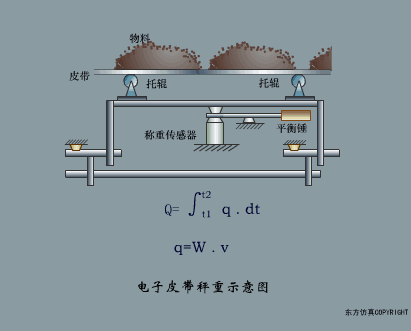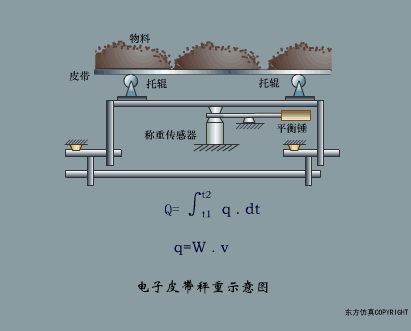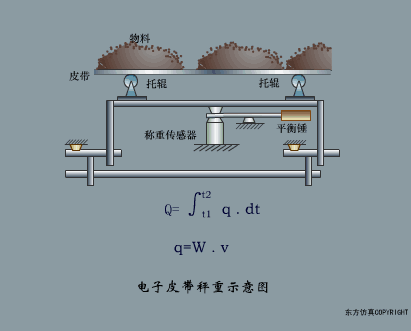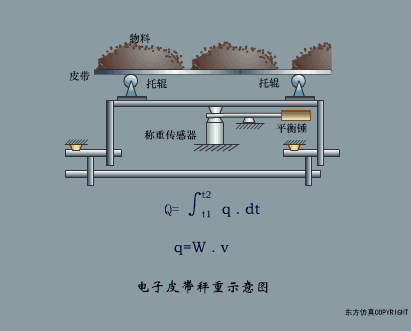
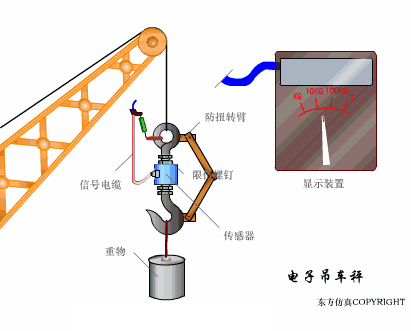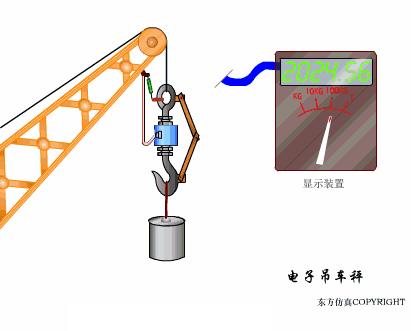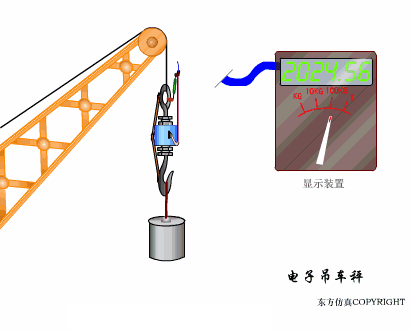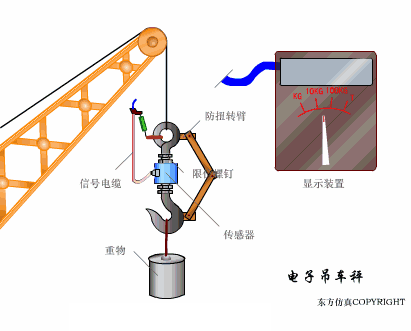
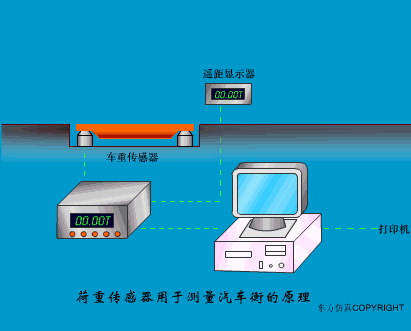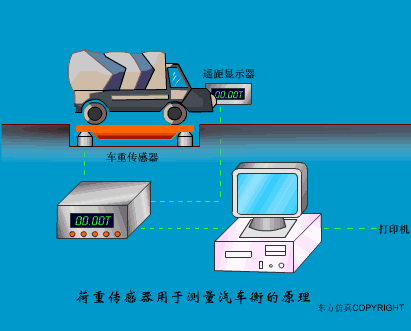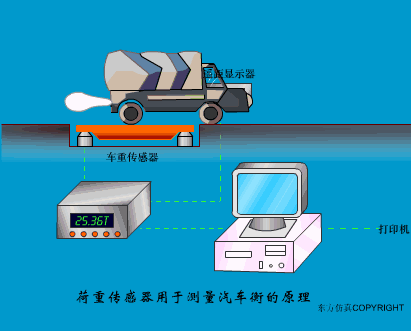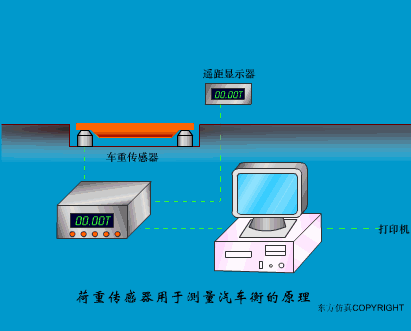
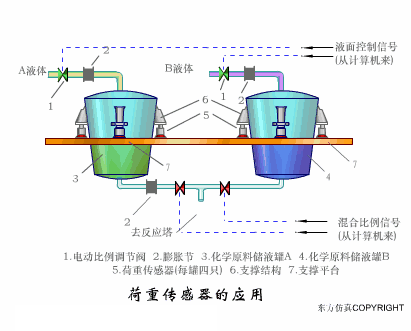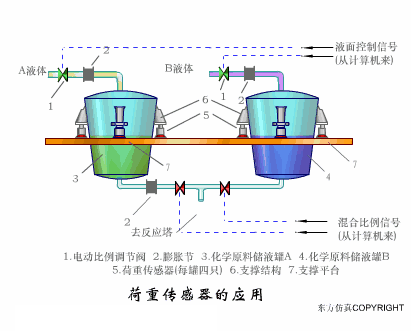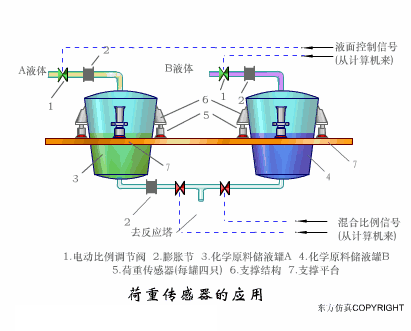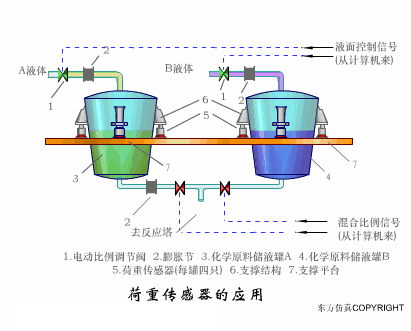
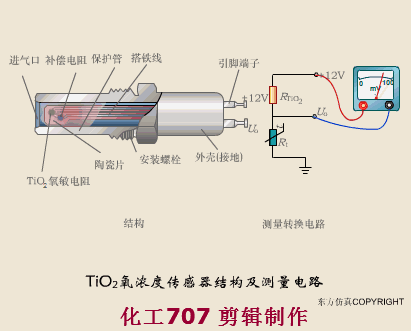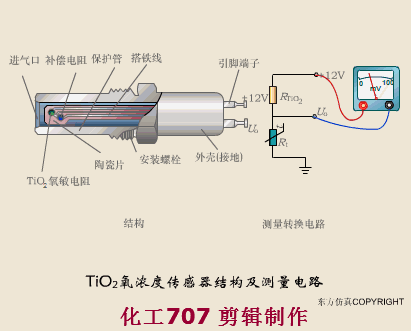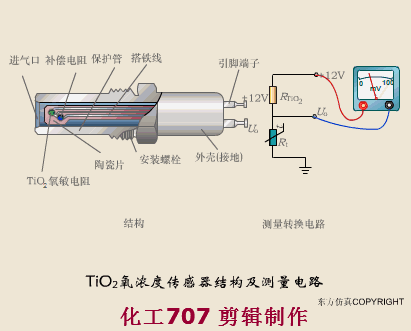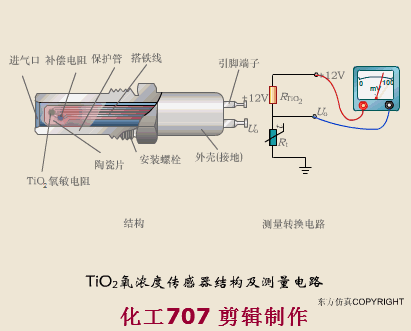
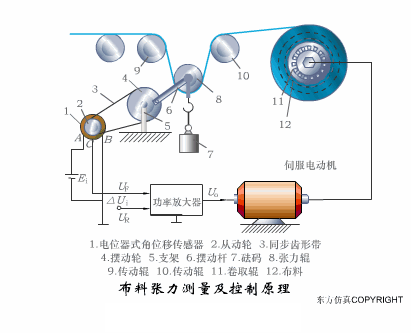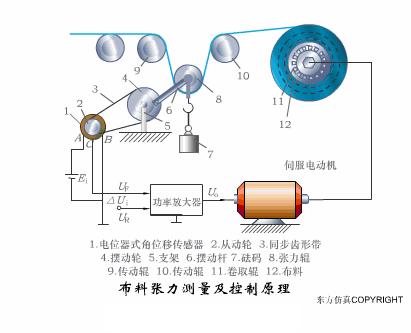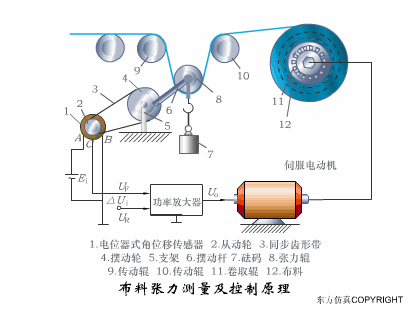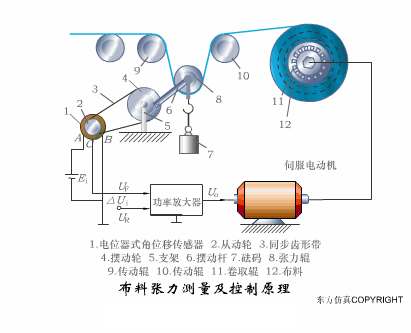
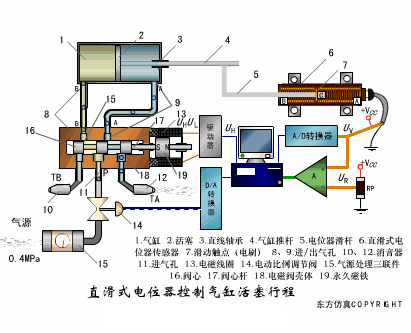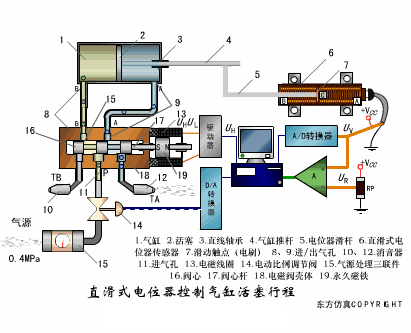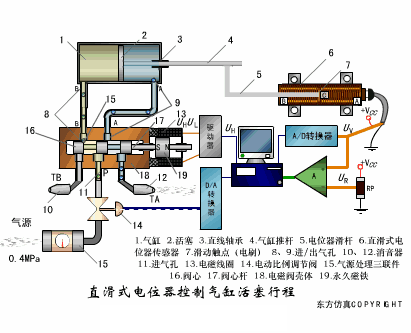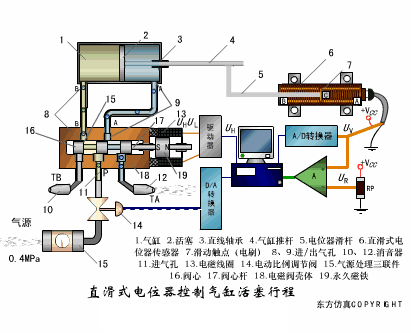
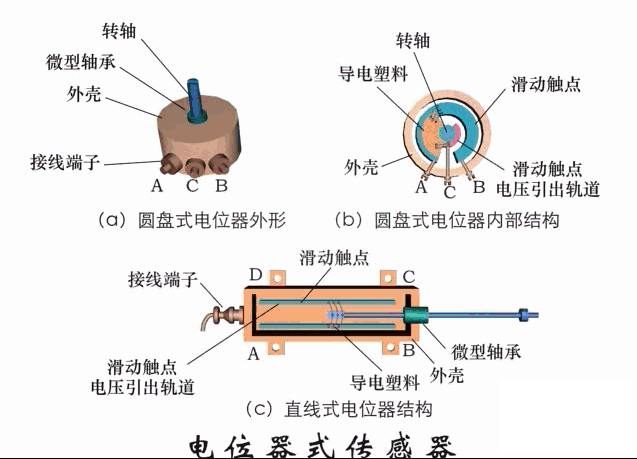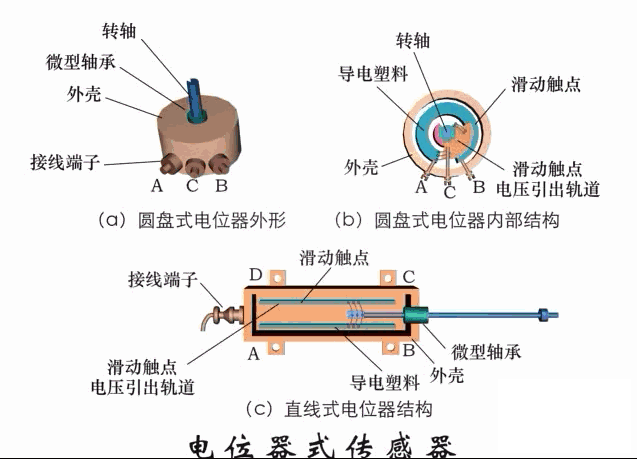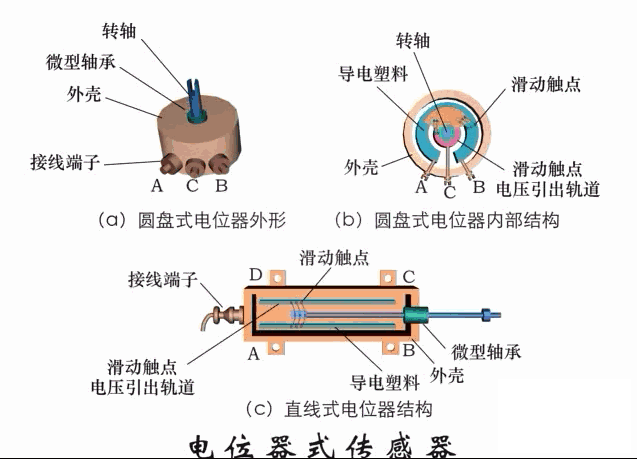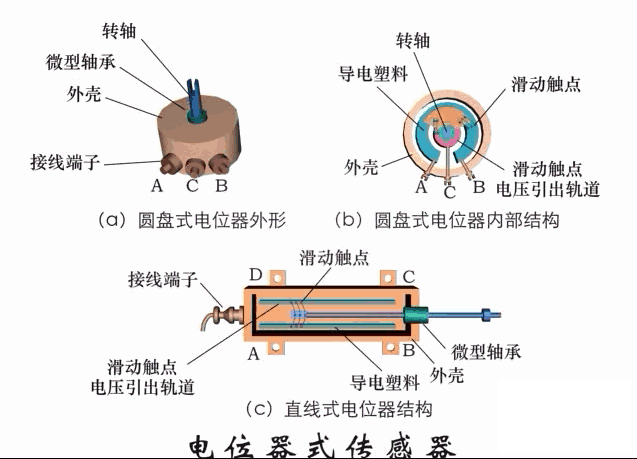
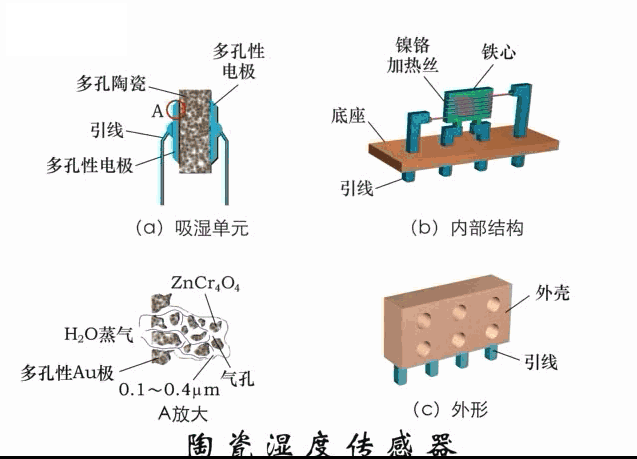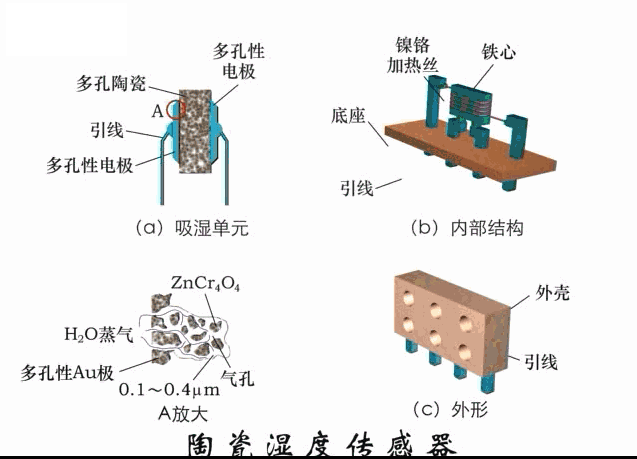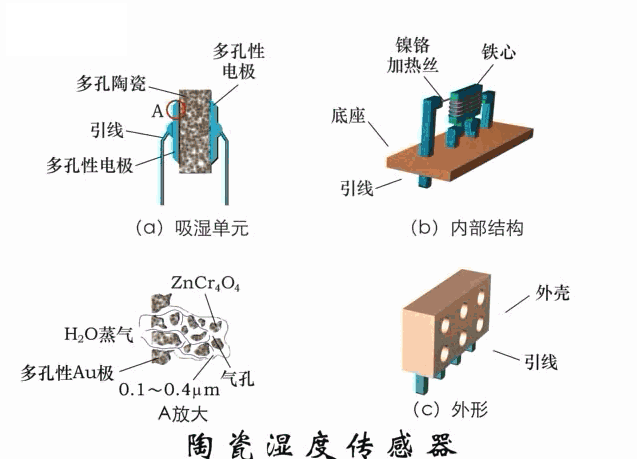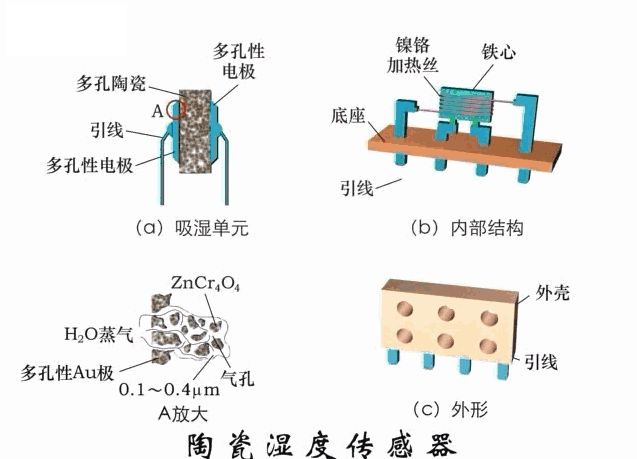
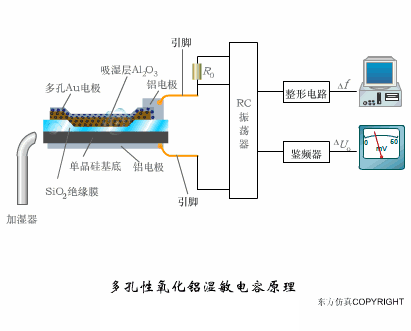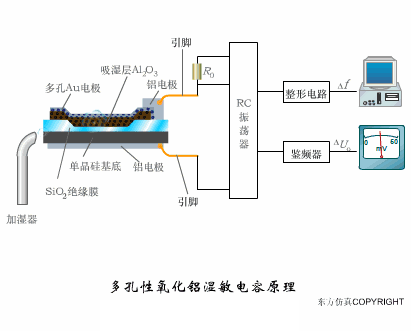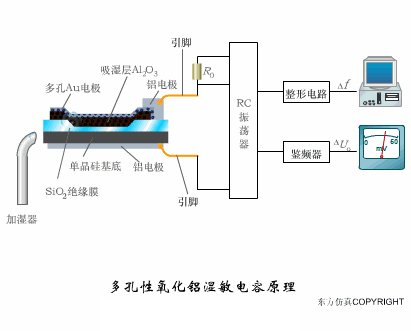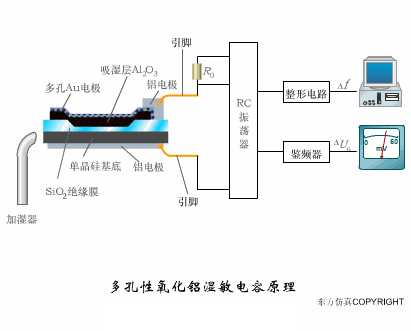
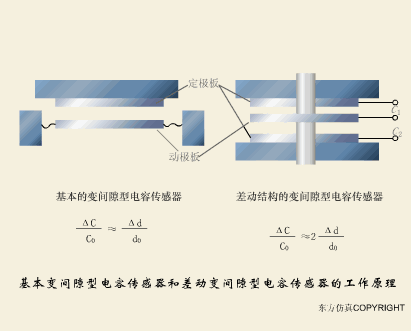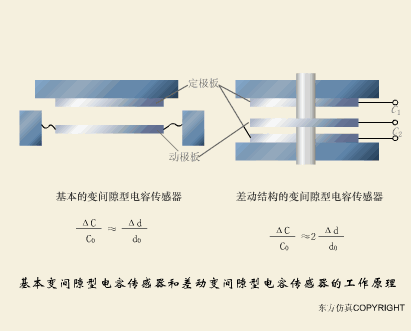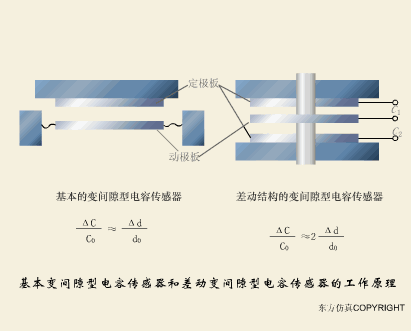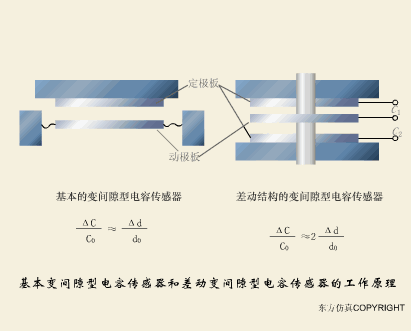
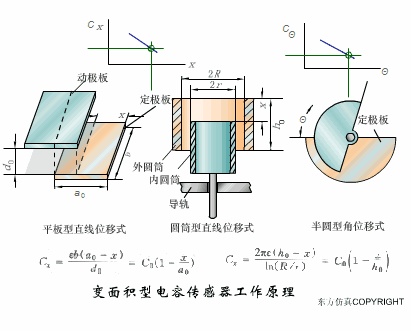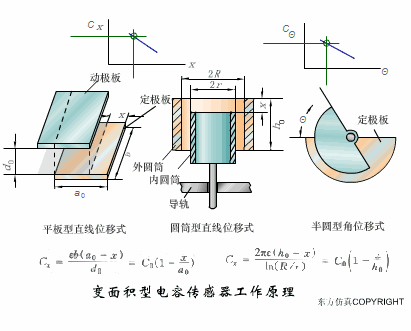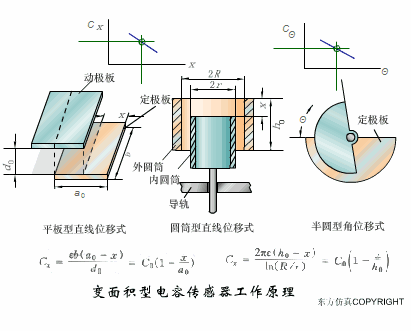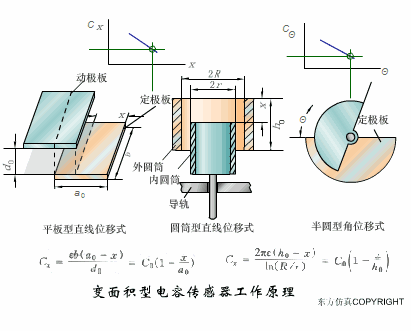
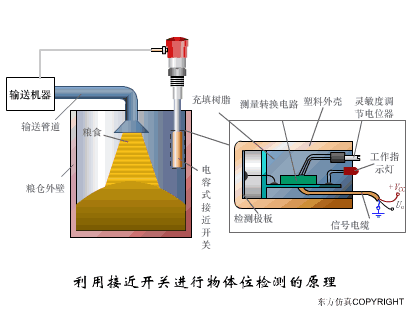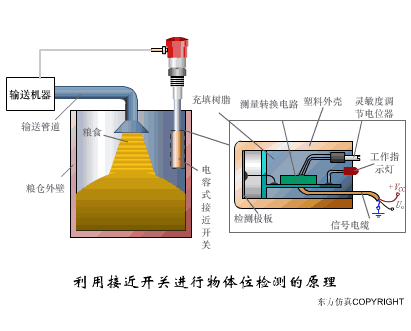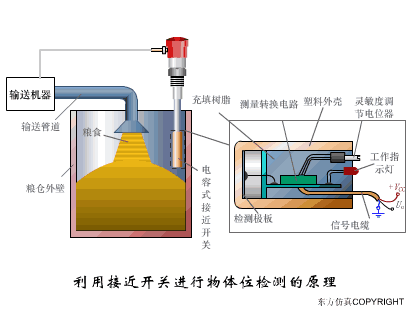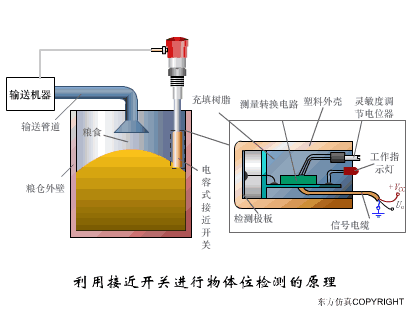
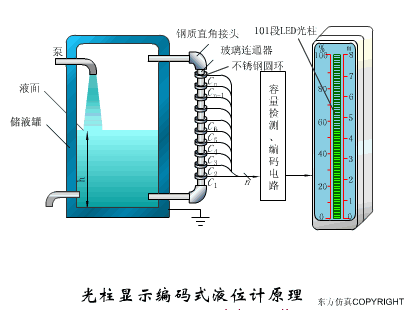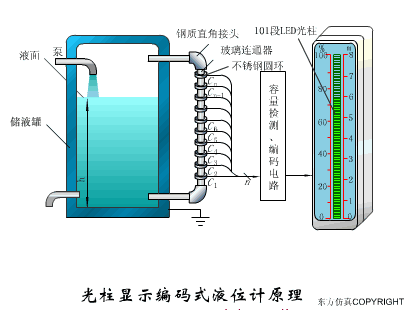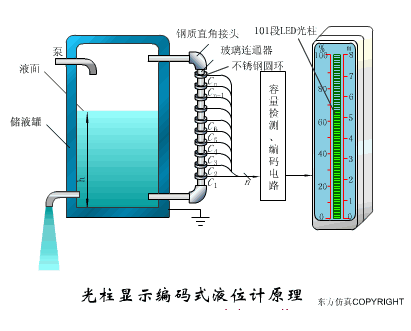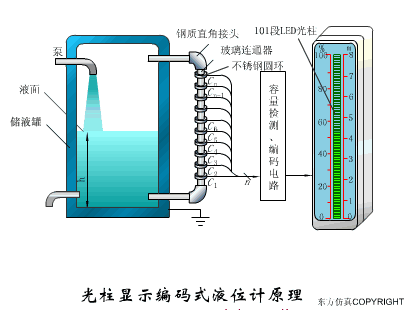
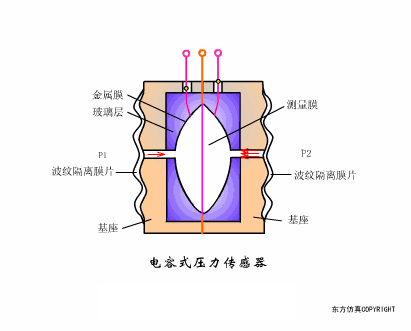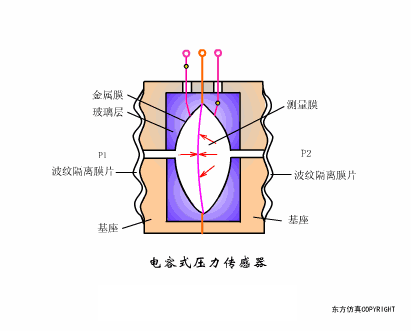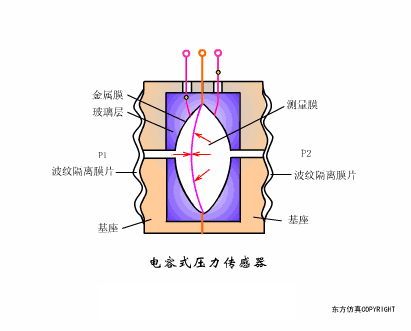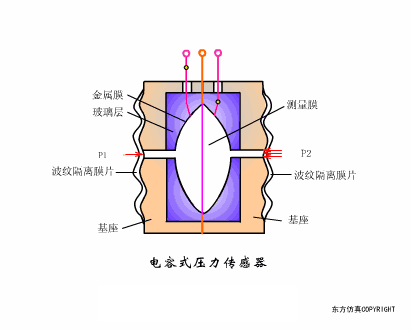
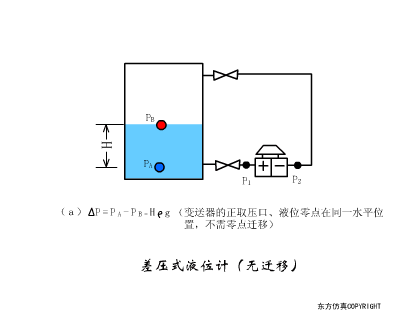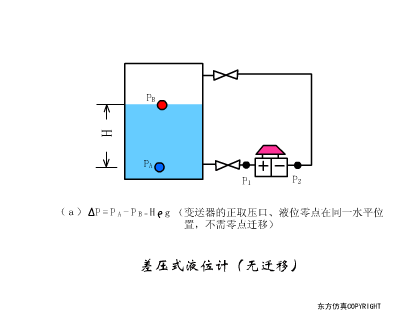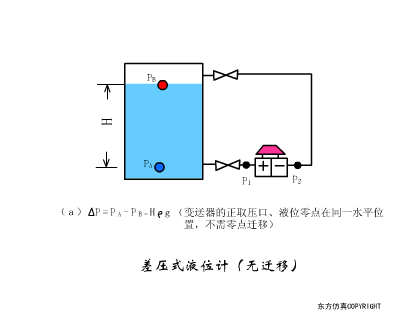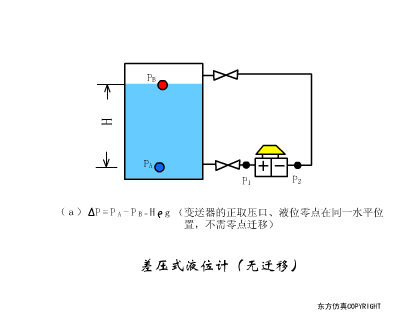
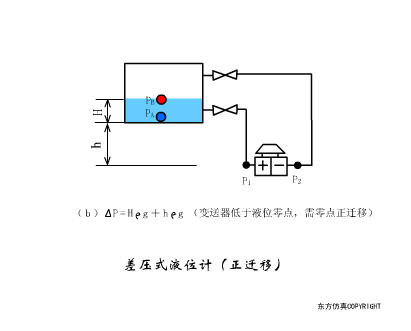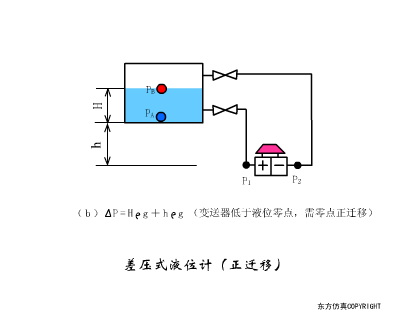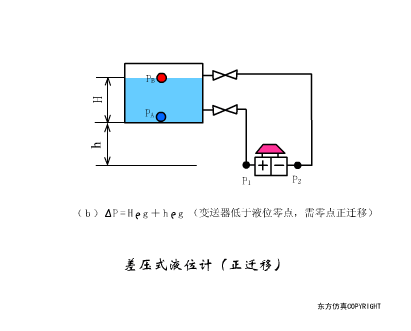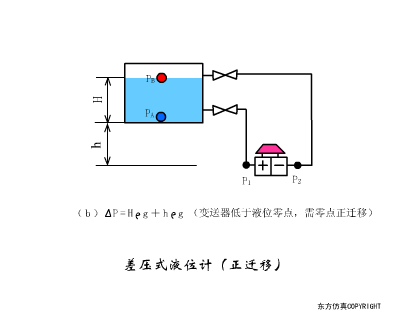
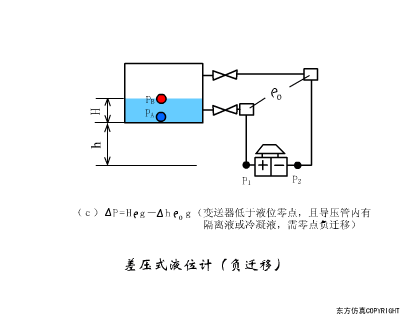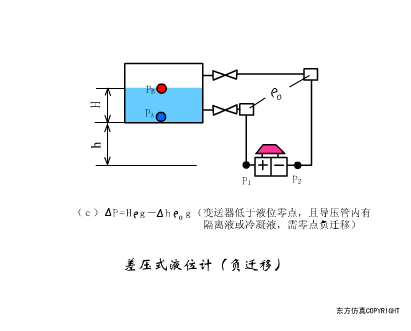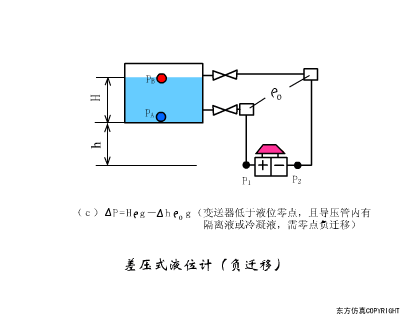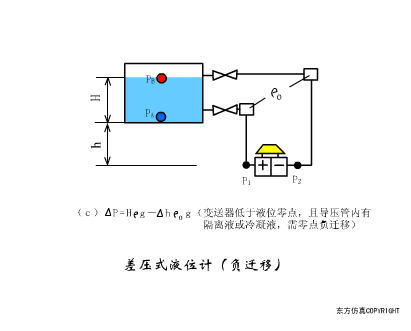
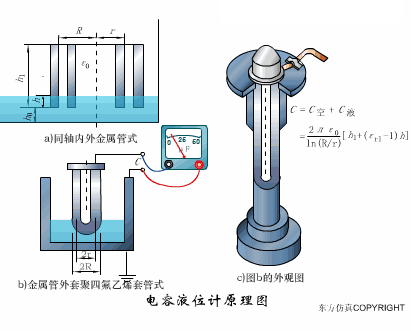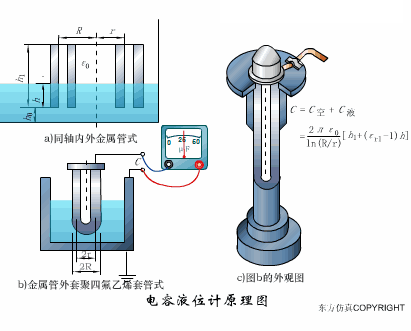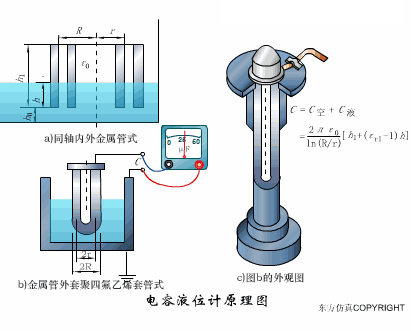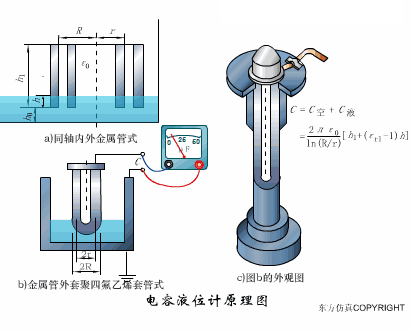
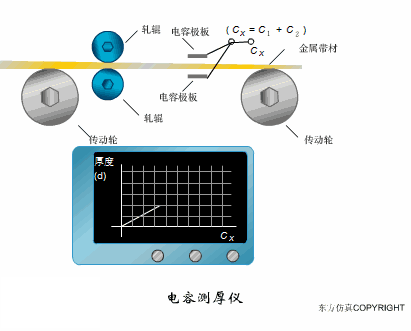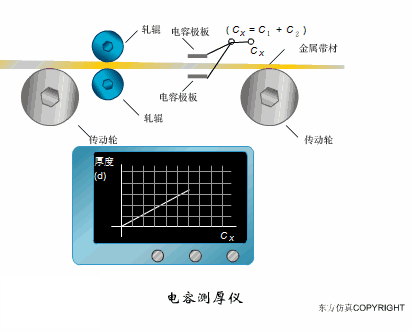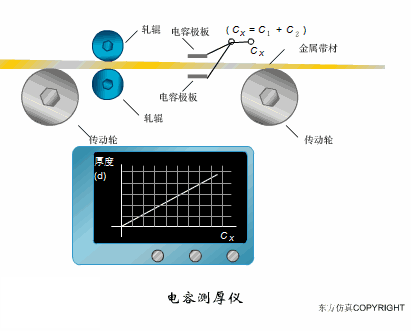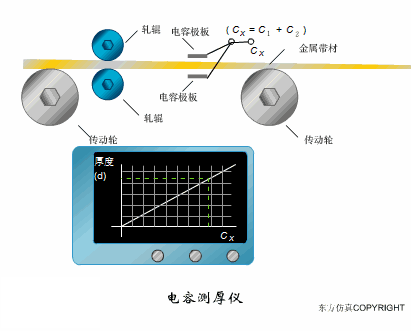
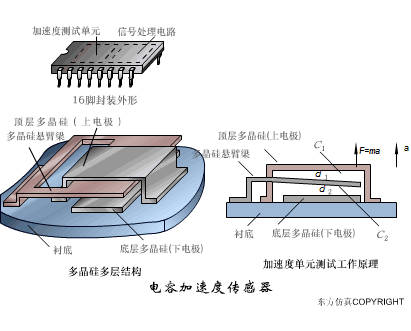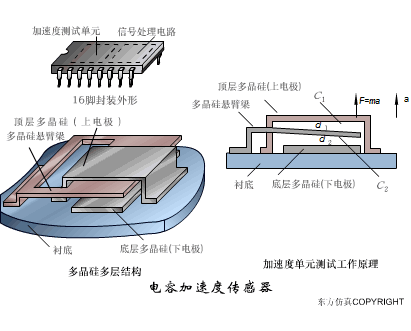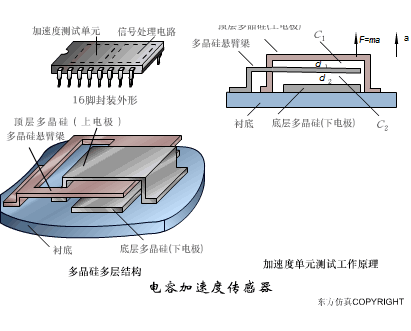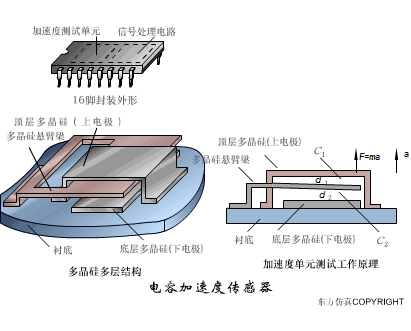
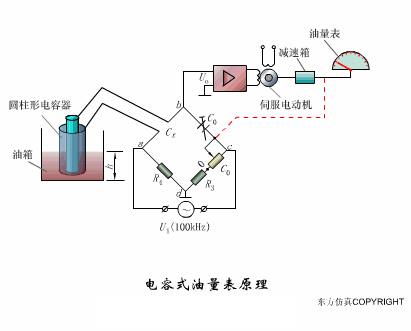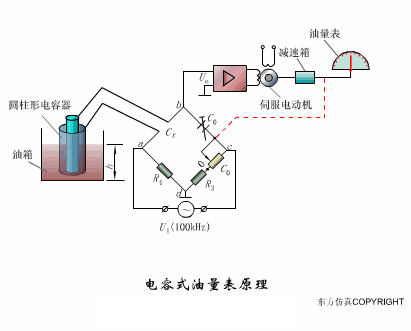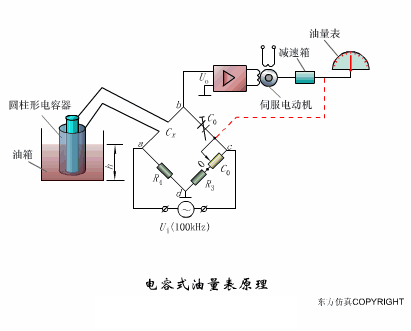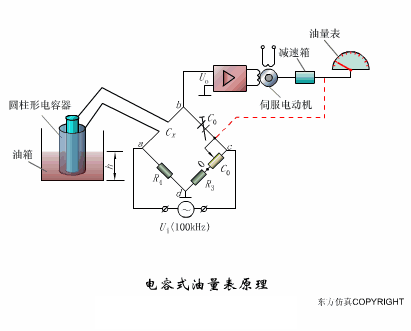
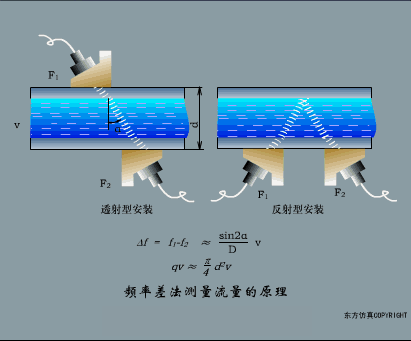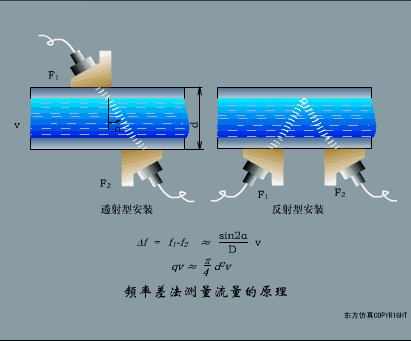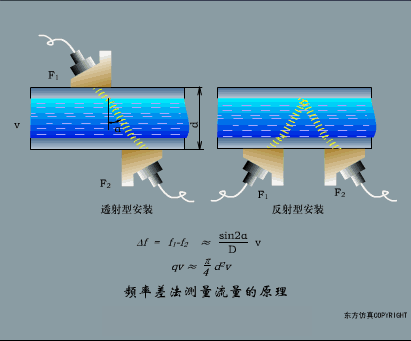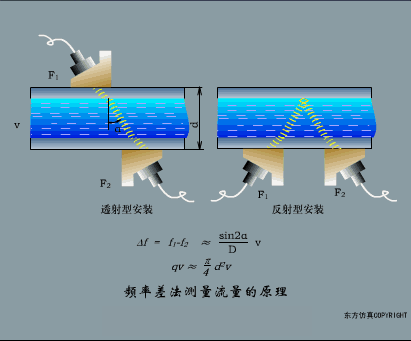
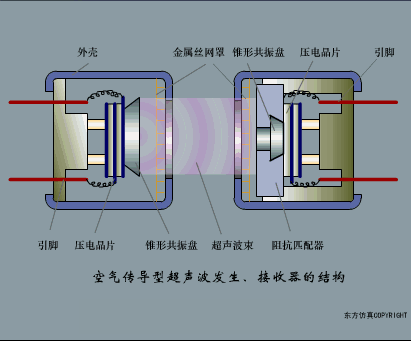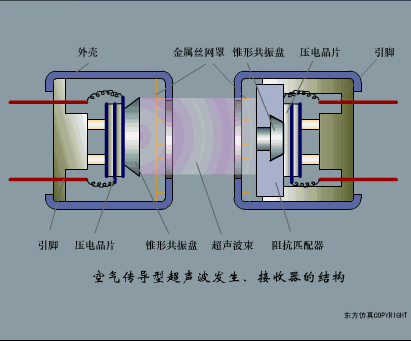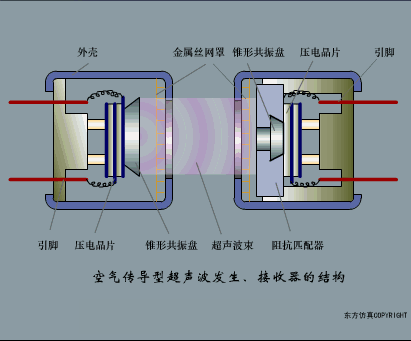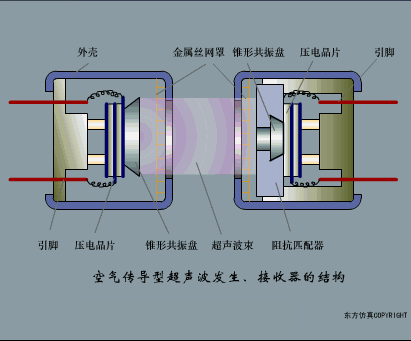
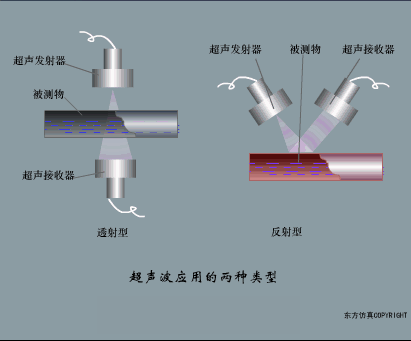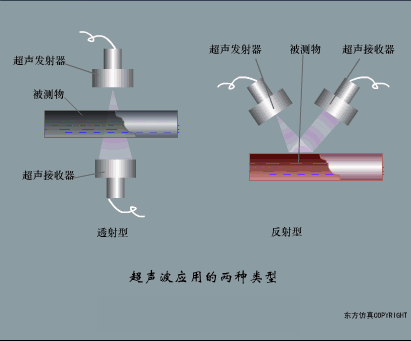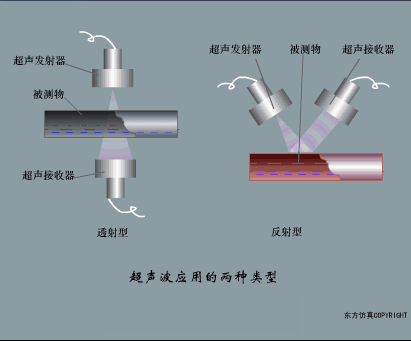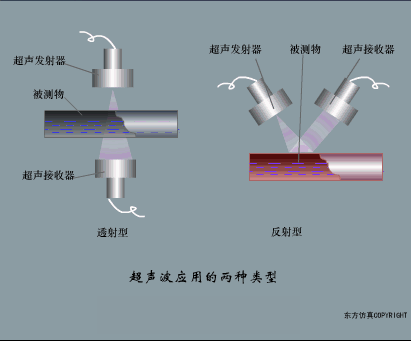
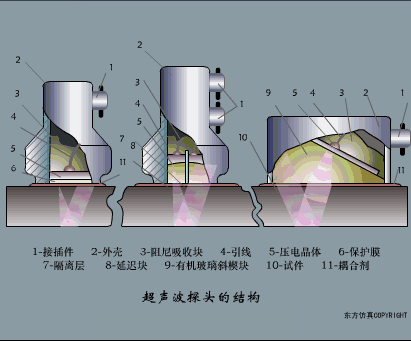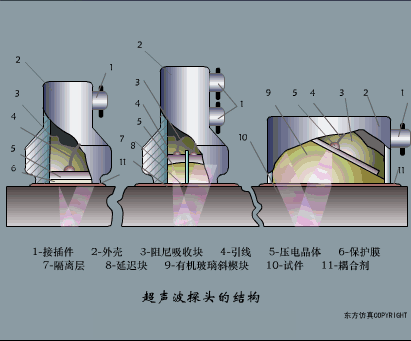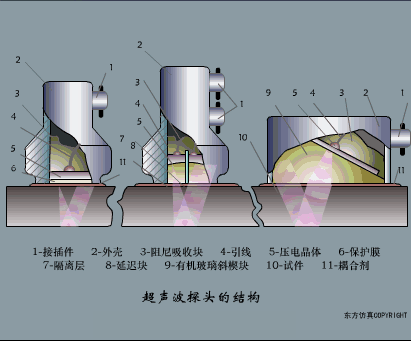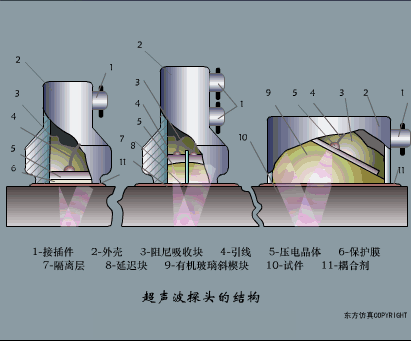
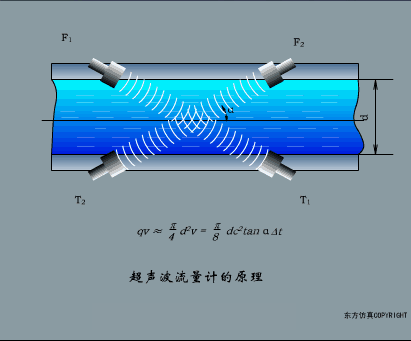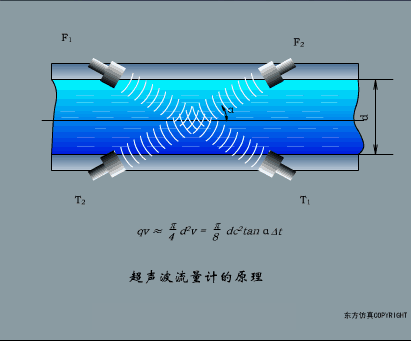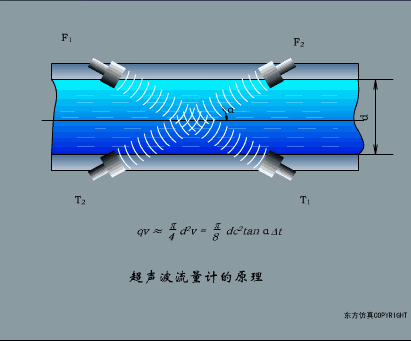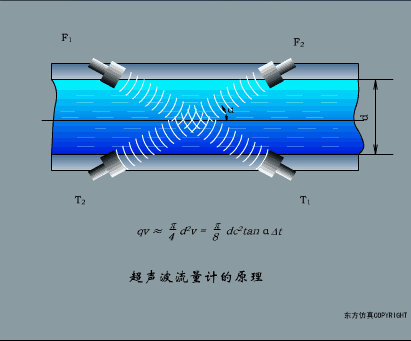
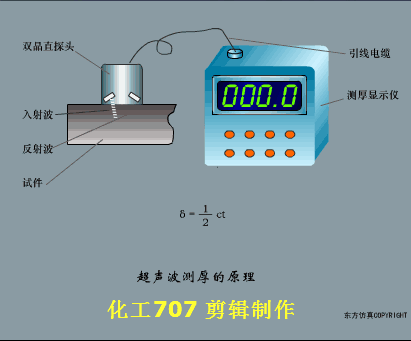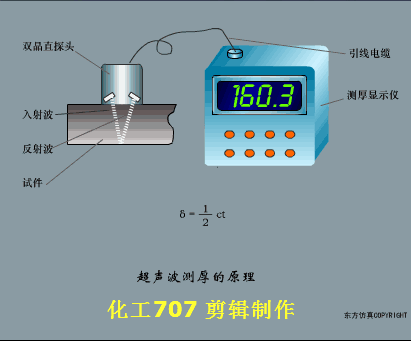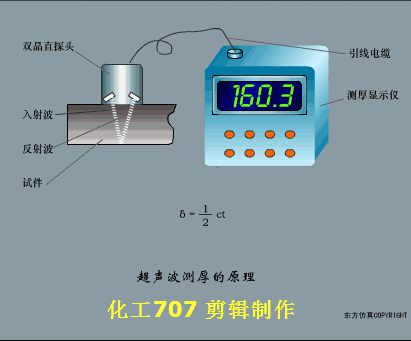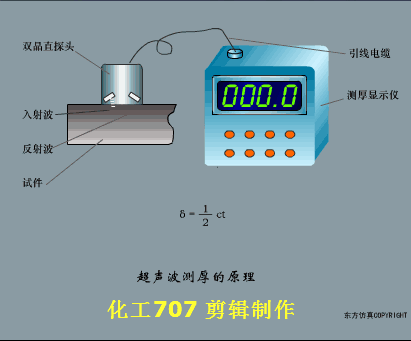
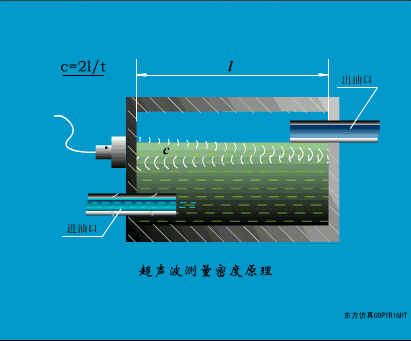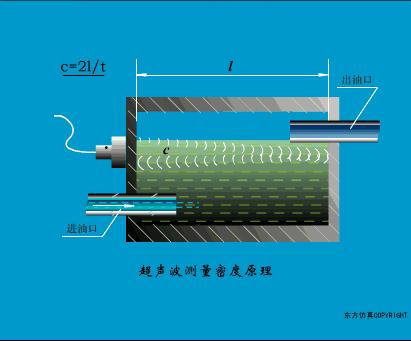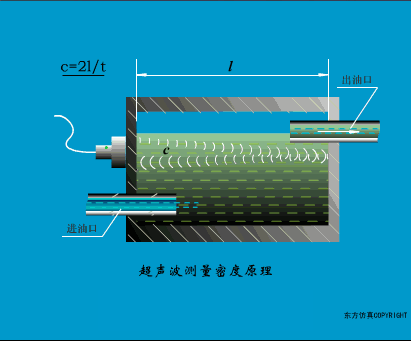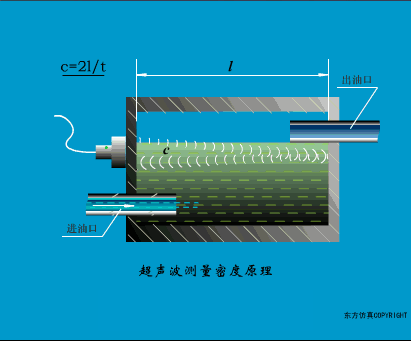
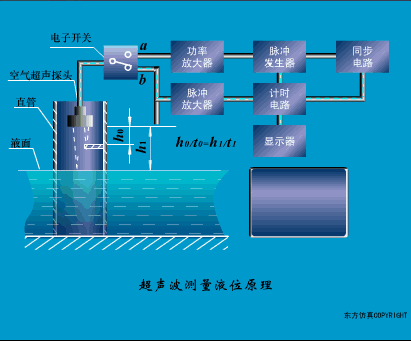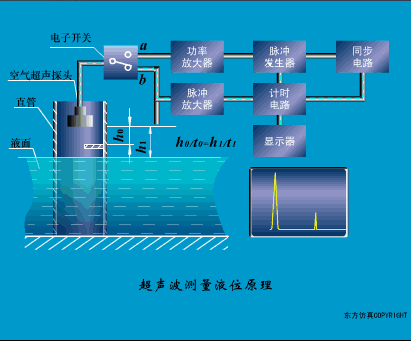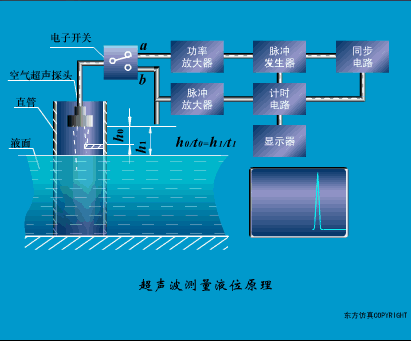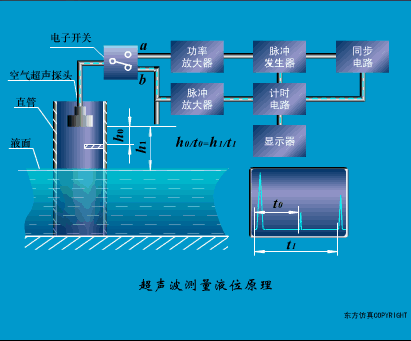
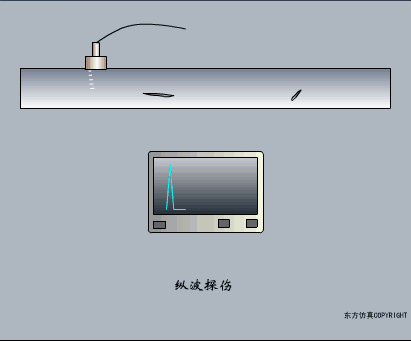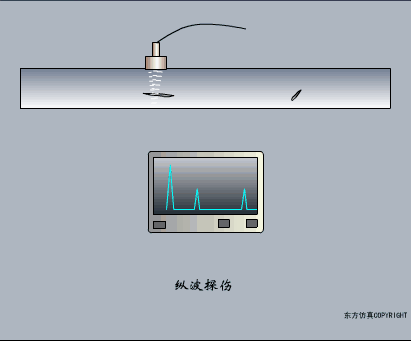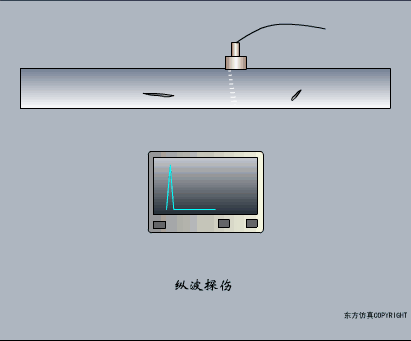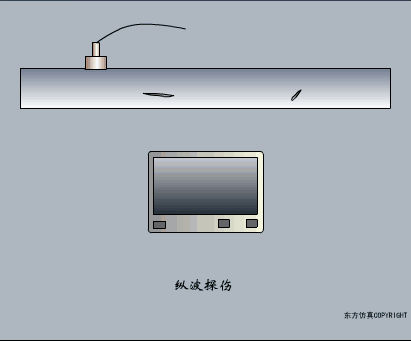
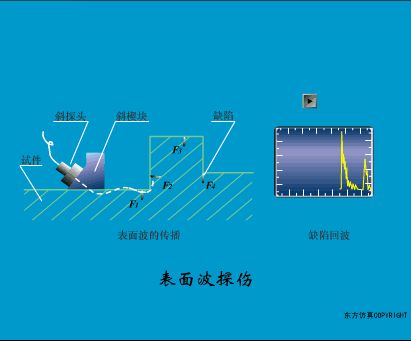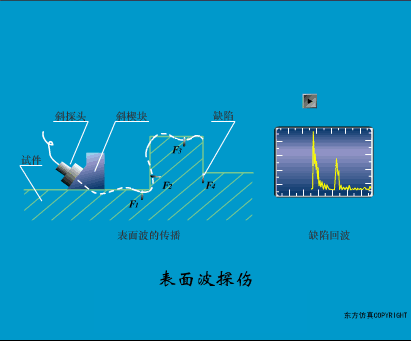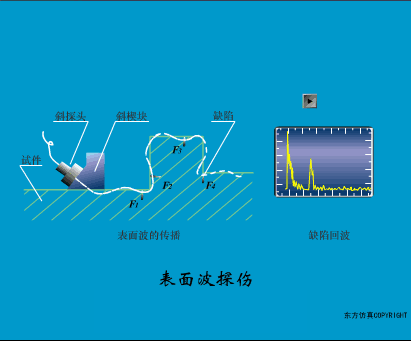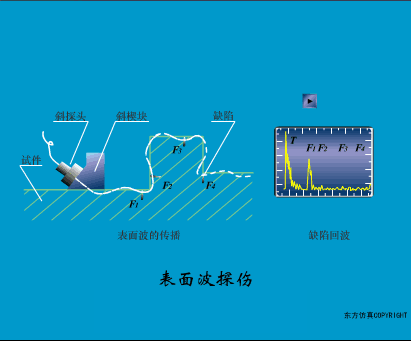
A sensor (English name: transducer/sensor) is a detection device that can sense the information being measured, and can transform the sensed information into electrical signals or other required forms of information output according to certain rules to meet the information Requirements for transmission, processing, storage, display, recording, and control. The characteristics of sensors include: miniaturization, digitization, intelligence, multi-function, systemization, and networking. It is the first link to realize automatic detection and automatic control. The existence and development of sensors give objects the sense of touch, taste and smell, and make objects slowly become alive. It is usually divided into ten categories according to its basic sensing function: heat sensitive elements, photosensitive elements, gas sensitive elements, force sensitive elements, magnetic sensitive elements, humidity sensitive elements, sound sensitive elements, radiation sensitive elements, color sensitive elements and taste sensitive elements. . The working principle of piezoresistive sensor measuring liquid level â–¼ MQN type gas sensitive resistor structure and measuring circuit â–¼ The working principle of bubble level â–¼ Diffused silicon pressure sensor â–¼ Strain acceleration sensor â–¼ Weighing type level gauge â–¼ Electronic belt weighing diagram â–¼ Electronic crane scale â–¼ The principle of load cell used to measure truck scale â–¼ Application of load cell â–¼ TiO2 oxygen concentration sensor structure and measuring circuit â–¼ Fabric tension measurement and control principle â–¼ Direct sliding potentiometer controls the cylinder piston stroke â–¼ Potentiometer sensor â–¼ Ceramic humidity sensor â–¼ Principle of Porous Alumina Humidity Capacitor â–¼ Basic variable gap type capacitance sensor and Working Principle of Differential Variable Gap Capacitance Sensor â–¼ Working principle of variable area capacitive sensor â–¼ The principle of object position detection using proximity switches â–¼ The principle of coded level gauge with light beam display â–¼ Capacitive pressure sensor â–¼ Differential pressure level gauge a â–¼ Differential pressure level gauge b â–¼ Differential pressure level gauge c â–¼ Capacitance level gauge schematic diagram â–¼ Capacitance Thickness Gauge â–¼ Capacitive acceleration sensor â–¼ Principle of Capacitive Fuel Gauge â–¼ The principle of frequency difference method to measure flow â–¼ Structure of air conduction ultrasonic generator and receiver â–¼ Two types of ultrasonic applications â–¼ The structure of the ultrasonic probe â–¼ The principle of ultrasonic flowmeter â–¼ The principle of ultrasonic thickness measurement â–¼ Principle of Ultrasonic Density Measurement â–¼ Principle of ultrasonic level measurement â–¼ Ultrasonic anti-theft alarm â–¼ Longitudinal wave inspection â–¼ Transverse wave inspection â–¼ Surface wave inspection â–¼ Various Puffs Vape,Disposable Vape Etsy,Allo Disposable Vape,Various Puffs Vape Atomizer Lensen Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.lensenvape.com